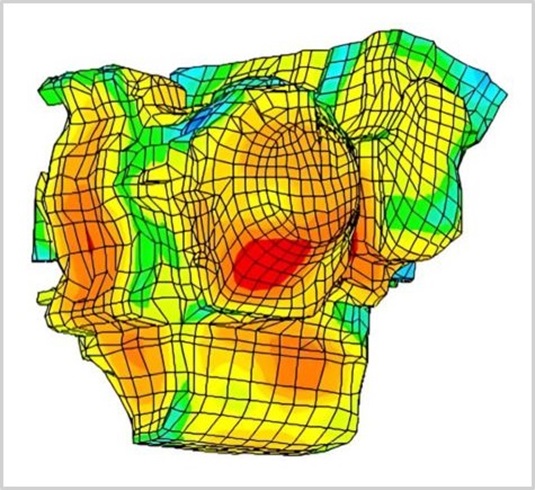
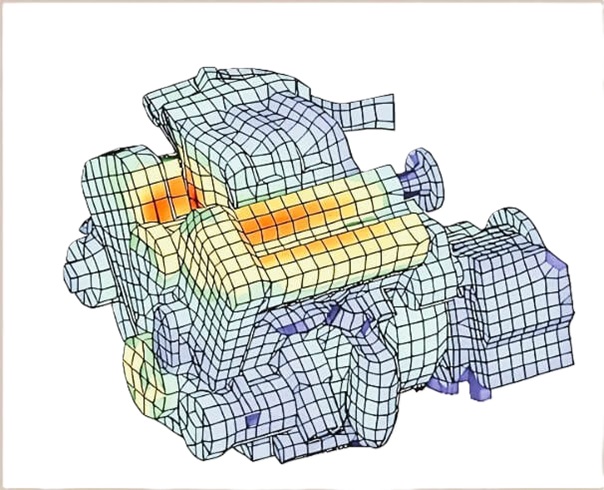
Benefits
Ease of Modeling
Requires only the modeling of the boundary of the acoustic domain. This results in reduced
effort to create representative models.
Exact Modeling of Interior and Acoustic Domains
It uses the same model for both interior and exterior domains. Unlike domain based methods such as
finite element methods, it uses exact representation of the integral
equation for the modeling of the exterior domains.
Ease of post response analysis
Responses within the acoustic domains are evaluated post-analysis after the solution of
the boundary value problems. Thus, the addition of response locations does not require the re-solution
of the boundary value problem.